Introduction
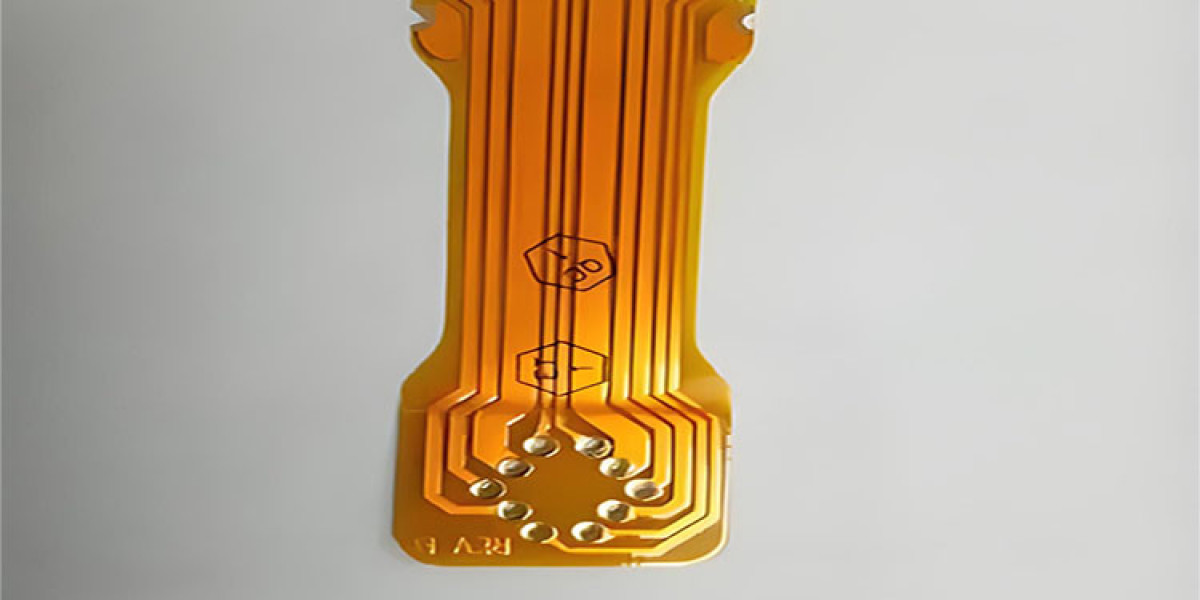
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) boards, made from polyimide or polyester film substrates, are highly regarded for their high wiring density, lightweight, and thin profile. These boards find extensive applications in mobile phones, tablets, medical devices, LEDs, automotive electronics, and wearable technology. FPCs are categorized into single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, and rigid-flex FPCs.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Types of FPCs
- Single-Sided FPC
- Double-Sided FPC
- Multilayer FPC
- Rigid-Flex FPC
3. Single-Sided FPC
- Without Coverlay
- With Coverlay
- Double-Sided Connection Without Coverlay
- Double-Sided Connection With Coverlay
4. Double-Sided FPC
5. Multilayer FPC
- Flex Insulating Base Finished Product
- Soft Insulating Base Finished Product
6. Rigid-Flex FPC
7. Conclusion
Types of FPCs
Single-Sided FPC
Single-sided FPCs feature a single conductive pattern layer created through chemical etching, with the conductive pattern layer typically made of rolled copper foil. The insulating substrate can be polyimide, polyester, aramid, or PVC. There are four subtypes of single-sided FPCs:
1. Without Coverlay
The conductor pattern is on the insulating substrate without a cover layer. Connections are achieved through soldering, welding, or pressure welding.
2. With Coverlay
Similar to the above but with an added cover layer over the conductor pattern, leaving the pads exposed. Simple designs may have uncovered end regions.
3. Double-Sided Connection Without Coverlay
Connection pads are accessible on both sides of the conductor pattern. The insulating substrate has through holes for connections, created by punching, etching, or mechanical methods.
4. Double-Sided Connection With Coverlay
This type has a cover layer with through holes, allowing connections on both sides while maintaining the cover layer. It comprises two layers of insulating material and a metal conductor.
Double-Sided FPC
Double-sided FPCs feature conductive patterns etched on both sides of an insulating film, increasing wiring density per unit area. Metalized holes connect patterns on both sides, forming a conductive path that enhances design flexibility and functionality. The cover film protects the single or double-sided conductors and indicates component placement.
Multilayer FPC
Multilayer FPCs consist of three or more layers of single or double-sided flexible circuits laminated together. Metalized holes formed through drilling and plating create conductive paths between layers. This design eliminates complex welding processes and offers lightweight, excellent electrical properties. Multilayer FPCs are further categorized into:
1. Flex Insulating Base Finished Product
Constructed on a flexible insulating substrate, designed to be bendable. Typically, multiple single or double-sided flexible circuits are bonded together at the ends but not in the central area, maintaining high flexibility.
2. Soft Insulating Base Finished Product
Built on a soft insulating substrate, these products are not specified to be bendable.
Rigid-Flex FPC
Rigid-flex FPCs combine flexible and rigid circuits through lamination and other processes to meet specific requirements. They retain the characteristics of both FPCs and rigid PCBs, featuring flexible and rigid regions. This design optimizes internal space, reduces product volume, and enhances performance, making them ideal for specialized applications.
Conclusion
FPCs are integral to modern electronics, offering unmatched flexibility, and lightweight, and compact design capabilities. Understanding the various types and their unique advantages helps in selecting the right FPC for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.